Urological Cancers
Urologic cancers are pertinent to the cancer of the organs of the urinary system and the male reproductive system. Urologic cancer is elaborated as the cancer of penile, bladder, kidney, testicles and prostate.
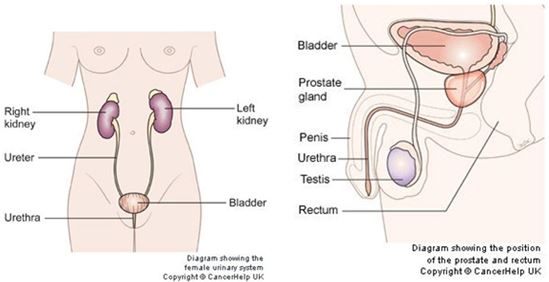
There are several types of urological cancer such as kidney and bladder cancer which is experienced by both male and female, while other gender specific like testicular and prostate cancer occurs in male and vaginal cancer happen in female.
Cancers specific to Males
- Penile cancer: It is the cancer found on the skin or within the tissues of the penis. The penile cancer is squamous cell cancer that can happen anywhere on the foreskin, the glans (head) of the penis or penile shaft. It can generally be cured, provided it is diagnosed early.
- Prostate cancer: The prostate is the gland below a man's bladder that produces fluid for semen. Prostate cancer is common among older men. It is rare in men younger than 40. Risk factors for developing prostate cancer include being over 65 years of age, family history, and being African-American.
Symptoms of prostate cancer may include
- Problems passing urine, such as pain, difficulty starting or stopping the stream, or dribbling
- Low back pain
- Pain with ejaculation
To diagnose prostate cancer, you doctor may do a digital rectal exam to feel the prostate for lumps or anything unusual. You may also get a blood test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA). These tests are also used in prostate cancer screening, which looks for cancer before you have symptoms. If your results are abnormal, you may need more tests, such as an ultrasound, MRI, or biopsy.
Treatment often depends on the stage of the cancer. How fast the cancer grows and how different it is from surrounding tissue helps determine the stage. Men with prostate cancer have many treatment options. The treatment that's best for one man may not be best for another. The options include watchful waiting, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy. You may have a combination of treatments.
Testicular cancer: Testicles, or testes, make male hormones and sperm. They are two egg-shaped organs inside the scrotum, the loose sac of skin behind the penis. You can get cancer in one or both testicles.
Testicular cancer mainly affects young men between the ages of 20 and 39. It is also more common in men who
- Have had abnormal testicle development
- Have had an undescended testicle
- Have a family history of the cancer
Symptoms include pain, swelling, or lumps in your testicles or groin area. Doctors use a physical exam, lab tests, imaging tests, and a biopsy to diagnose testicular cancer. Most cases can be treated, especially if found early. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy. Regular exams after treatment are important.
Treatments may also cause infertility. If you may want children later on, you should consider sperm banking before treatment.
Urological cancer that can occur in both male and female
Kidney cancer: kidneys are fist-sized organs on either side of your backbone above your waist. The tubes inside filter and clean your blood, taking out waste products and making urine. Kidney cancer forms in the lining of tiny tubes inside your kidneys.
Kidney cancer becomes more likely as you age. Risk factors include smoking, having certain genetic conditions, and misusing pain medicines for a long time.
You may have no symptoms at first. They may appear as the cancer grows. See your health care provider if you notice
- Blood in your urine
- A lump in your abdomen
- Weight loss for no reason
- Pain in your side that does not go away
- Loss of appetite
Treatment depends on your age, your overall health and how advanced the cancer is. It might include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation, biologic, or targeted therapies. Biologic therapy boosts your body's own ability to fight cancer. Targeted therapy uses substances that attack cancer cells without harming normal cells.
Bladder cancer: The bladder is a hollow organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer occurs in the lining of the bladder. It is the sixth most common type of cancer in the United States.
- Symptoms include
- Blood in your urine
- A frequent urge to urinate
- Pain when you urinate
- Low back pain
Risk factors for developing bladder cancer include smoking and exposure to certain chemicals in the workplace. People with a family history of bladder cancer or who are older, white, or male have a higher risk.
Treatments for bladder cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and biologic therapy. Biologic therapy boosts your body's own ability to fight cancer.
Adrenal cancer: It is also termed as adrenal glands cancer. Adrenal glands are located at the top of our each kidney. The treatment is available that cures adrenal glands comprehensively.
The urological cancers of bladder, prostate, kidney and testis are handled and treated by the team of urology surgeon, radiotherapists and medical oncologist.
